GSTC Mission and Impacts
GSTC Vision
Tourism fulfills its potential as a vehicle for social, cultural, and economic good while removing and avoiding any negative impacts from its activities in terms of environmental and social impacts.
GSTC Mission
To be an agent of change in the world of sustainable travel and tourism by fostering the increased knowledge, understanding, adoption and demand for sustainable tourism practices.
GSTC Activities & Impacts
Developing International Standards – the GSTC Standards
The GSTC Industry Standard, the GSTC Destination Standard, the GSTC MICE Standard and the GSTC Attraction Standard (known previously as GSTC Industry Criteria, GSTC Destination Criteria, GSTC MICE Criteria and GSTC Attraction Criteria) provide a comprehensive definition of sustainable travel and tourism. They are aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and are based on the four pillars of sustainability: (1) Managing for sustainability; (2) Social; (3) Culture and Community; (4) Environment.
GSTC Theory of Change
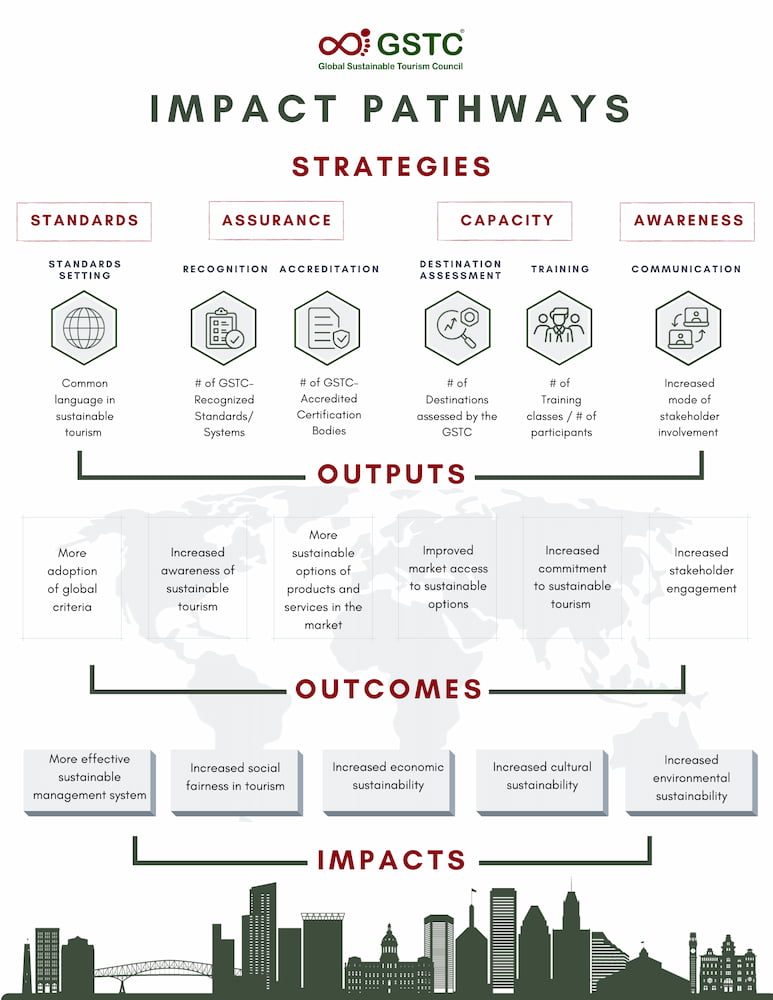 A Theory of Change serves as a comprehensive framework, detailing not only the desired change an organization or initiative aims to achieve but also elucidating the mechanisms by which its efforts facilitate this transformation. This conceptual map traces a causal pathway, linking the strategies employed (the actions taken) to the resulting outcomes (what has been changed), as well as the underlying assumptions of the process. GSTC’s Impact Pathways vividly illustrate these dynamic interconnections.
A Theory of Change serves as a comprehensive framework, detailing not only the desired change an organization or initiative aims to achieve but also elucidating the mechanisms by which its efforts facilitate this transformation. This conceptual map traces a causal pathway, linking the strategies employed (the actions taken) to the resulting outcomes (what has been changed), as well as the underlying assumptions of the process. GSTC’s Impact Pathways vividly illustrate these dynamic interconnections.
Intended Impacts & Outcomes
- Provide guidelines for businesses and destinations of all sizes and all over the world to become more sustainable
- Provide guidance for travelers and travel providers in choosing suppliers and sustainable tourism programs
- Provide a common denominator for media to recognize sustainable tourism providers
- Help certification and other voluntary programs ensure that their standards meet a broadly-accepted baseline
- Governmental, non-governmental and private sector programs have a framework for developing sustainable tourism requirements
- Provide guidelines for education and training bodies such as hotel schools and universities
Providing Assurance for Sustainable Tourism
Accreditation: GSTC accredits certification bodies that certify hotels, accommodations, tour operators, and destinations against relevant GSTC Standards or GSTC-Recognized standards and meet international requirements and tourism-specific requirements outlined in the GSTC Accreditation Manuals. This provides the marketplace a credible means of selecting Certification Bodies that have been verified by an impartial, credible assurance provider.
GSTC-Recognition: GSTC provides a formal indication of other standards that align with the GSTC Standards. GSTC-Recognized means that a sustainable tourism standard has been deemed equivalent to the GSTC Standards for sustainable tourism. This designation is made by GSTC’s expert, Recognition Decision-Making Committee. GSTC-Recognized refers to a standard and does NOT mean that the Certification Body using the standard is accredited.
What is the difference between certification and accreditation? Organizations get certified by a Certification Body, and Certification Bodies get accredited by an Accreditation Body. Both levels, certification and accreditation, exist to provide evidence of neutrality and competence in the process of certification.
Intended Impacts & Outcomes
 Accreditation drives market-facing ecolabel which supports Responsible Consumption & Production by giving buyers of tourism services at both the retail and wholesale level a credible means of selecting services and suppliers that are certified sustainable.
Accreditation drives market-facing ecolabel which supports Responsible Consumption & Production by giving buyers of tourism services at both the retail and wholesale level a credible means of selecting services and suppliers that are certified sustainable.- GSTC has impacted the uptake of certification by enhancing its credibility in a market that suffers from confusion of 250+ standards. For example, TUI has certified nearly 400 of its owned hotels from 2014 to 2020 with a requirement that the Certification Bodies selected by each hotel use a GSTC-Recognized standard. Another example is the Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group, by 2025 all Mandarin Oriental properties will be GSTC-Certified.
- The GSTC Accreditation Manual has impacted non-accredited certification programs in tourism by raising awareness on impartiality requirements and other aspects of credible certification per the ISEAL Alliance Assurance Code and relevant ISO standards such as ISO 17065. GSTC has evidence of such impacts via direct communications with several programs’ leaders.
- Sustainability is defined similarly by participating programs by including the 4 pillars of the GSTC Standards. Further, Recognized standards include principles derived from GSTC’s intensively inclusive standards-setting processes. To date, some 66 standards are GSTC-Recognized, distributed throughout the world including many national programs.
- Some of the standards in use in tourism, including some of the most prominent and high volume programs, revised their standards from environment only to include social and other elements in order to gain GSTC-Recognized status. A prominent example is Green Key FEE, which at the behest of TUI Group and GSTC revised their standard in that manner 2015-2016. They are the largest by volume certifier in Europe.
- Impacts from the certification of hotels was measured in a survey conducted in 2017 by TUI Group, with a proper control group and other appropriate survey techniques, finding that hotels with sustainability certifications vs non-certified hotels achieved:
- 10% lower CO2 emissions per guest night
- 24% lower waste volume per guest night
- 19% less fresh water use per guest night
- 15% less total water use per guest night
- 23% higher use of green energy
- 9% higher employment rate of national employees
- Higher customer satisfaction scores for accommodation overall
Making Destinations Sustainable
Destination stewardship is a process by which local communities; governmental agencies, NGOs, and the tourism industry take a multi-stakeholder approach to maintaining the cultural, environmental, economic, and esthetic integrity of their country, region, or town. In other words, to ensure that the destination retains and enhances the distinctive attributes that make it attractive to beneficial tourism. The GSTC developed the GSTC Destination Standard and subsequent programs to help destinations apply the Standards to their destination management programs: Destination Certifications; Destination Assessments; Advisory Services for policymakers; Destination Stewardship Training – customized training programs for local destination management teams and key stakeholders; Destination Stewardship Report – a quarterly journal of global case studies.
Intended Impacts & Outcomes

Certification rewards exceptional players for achievement. Currently, 30 destinations are certified to the GSTC Destination Standard.
- Destination assessments provide reports as tools for continuous improvement. GSTC with partner support has conducted more than 40 comprehensive assessments globally.
- Intended impacts from all GSTC destination activities include community support for the visitor economy, conservation of environmental and cultural resources in the communities visited, minimized social disruption from touristic activities, and the economic benefits are optimized in terms of overall volume and in dispersal of those benefits to broad segments of the community.
- Evidence of impacts includes the fact that the 3 most recent winners of the most credible global award for destination stewardship, the WTTC Tourism for Tomorrow Awards, honored destinations that put the GSTC Standard into practice: 2019 St Kitts and Nevis Islands, 2018 Thompson-Okanagan Tourism Authority of British Columbia, Canada, and 2017 Okavanga Delta of the Botswana Tourism Organization.
- GSTC provides advisory service to governments on compliance with our standards. In 2020, eight national programs formally engaged GSTC for guidance in the development of national policy and implementation.
Market Access for sustainable tourism products and services
The GSTC promotes the development of broad market adoption and application of the GSTC Standards. With the ultimate goal of increasing demand for sustainable travel and tourism offerings and building trust amongst travelers, the GSTC works to identify opportunities and solutions for alignment greater market potential. For this, we work closely with prominent Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) on marking hotels that are certified in search results. We also work as with large travel providers for preferred contracting of certified hotels and tour operators.
Intended Impacts & Outcomes
 Outbound tour operators, cruiselines, and other buyers of local tour operations services select suppliers that strive to operate more sustainably. From 2016 many cruiseline brands practice preferential contracting with land tour operators that are certified sustainable. For example, Royal Caribbean measures and promotes land tours from their cruise ships that are operated by certified tour operators; their target of 1,000 tours per year by 2020 was already exceeded in 2018 and reach 2,014 in 2019.
Outbound tour operators, cruiselines, and other buyers of local tour operations services select suppliers that strive to operate more sustainably. From 2016 many cruiseline brands practice preferential contracting with land tour operators that are certified sustainable. For example, Royal Caribbean measures and promotes land tours from their cruise ships that are operated by certified tour operators; their target of 1,000 tours per year by 2020 was already exceeded in 2018 and reach 2,014 in 2019.- Buyers of hotel space at the retail and wholesale level select hotels that are certified sustainable. From 2014 to 2020 TUI Group certified most of their group-owned hotels and are now practicing preferential contracting non-owned hotels.
- Tour Operators give preference to more frequent and/or longer visits to destinations that are certified sustainable.
- Booking.com, Agoda.com, and Hotelbeds developed guidance to hotels on sustainability based on the GSTC Standards and are developing plans to provide consumers with indicators in search results of certified hotels.
- The Leading Hotels of the World (LHW) has introduced the Sustainability Leaders collection, recognizing over 50 of its luxury hotels across 80 countries committed to preserving the environment and cultural heritage through GSTC-Accredited certification or certification to a GSTC-Recognized Standard.
Increasing Knowledge
The GSTC is committed to ensuring that sustainable tourism best practices are adopted and implemented by the industry and the traveling public. The GSTC Sustainable Tourism Training Program (STTP), with the support of the Education and Training Working Group, is tasked with developing and identifying the tools and resources to facilitate the transition to sustainable practices, and delivering training classes for a wide range of tourism industry professionals including: hotel and tour operators, destination managers, government officials, resource managers, educational consultants, and academic institutions. GSTC offers online and offline training courses on Sustainable Tourism, Sustainable Hotels, and Sustainable Business Travel.
Intended Impacts & Outcomes
 Tourism leaders and practitioners gain better understanding of the breadth and depth of sustainability.
Tourism leaders and practitioners gain better understanding of the breadth and depth of sustainability.- Knowledge platforms are made available in all regions of the world and in many languages.
- Current program continues to expand both participant-paid sessions and organization-funded group sessions. During 2022, GSTC trained 1,425 participants on all six continents in 62 on-site and online courses.
- Program is now expanding to offer Sustainable Hotels training and Sustainable Business Travel training.
